We’re going to show you how marketing mix modeling works, why it’s needed, plus the pros and cons of using it to assess your marketing efforts.
Marketing mix modeling is making a comeback in the world of digital marketing.
With the rise of data walled gardens and the death of the cookie, marketers are finding it increasingly difficult to measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
MMM has been rediscovered as a way to overcome these challenges by providing marketers with a more holistic view of their marketing performance.
There’s no doubt that MMM will play a key role in the future of marketing measurement. If you’re a marketer, now is the time to start learning about and adopting this technology—and this article will help you get a head start.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
💡 Pro Tip
Chances are you’re here because you’ve considered using marketing mix modeling. If so, why not give Ruler Analytics a try? Ruler takes the best of marketing mix modeling and multi-touch attribution to give you the bigger picture and help you understand the factors that affect your sales, deals and ROI.
Book a demo to see Ruler’s MMM in action
Marketing mix modeling (MMM) is a statistical analysis technique used by companies to evaluate the impact of each marketing input on consumer behavior, sales and ROI.
The concept “marketing mix” was first coined in the 1960s, and marketing mix modeling as a formal analytical technique was developed and popularised in the 1980s and 1990s by marketing experts.
In recent years, marketing mix modeling has made a comeback in digital due to the challenges we face around Apple’s privacy changes, data walled gardens and third-party cookie tracking.
MMM breaks down your results by channel, allowing you to see which marketing activities are having the most significant impact on your desired outcomes.
It includes several variables to evaluate the impact and effectiveness of your marketing efforts. These variables typically include:
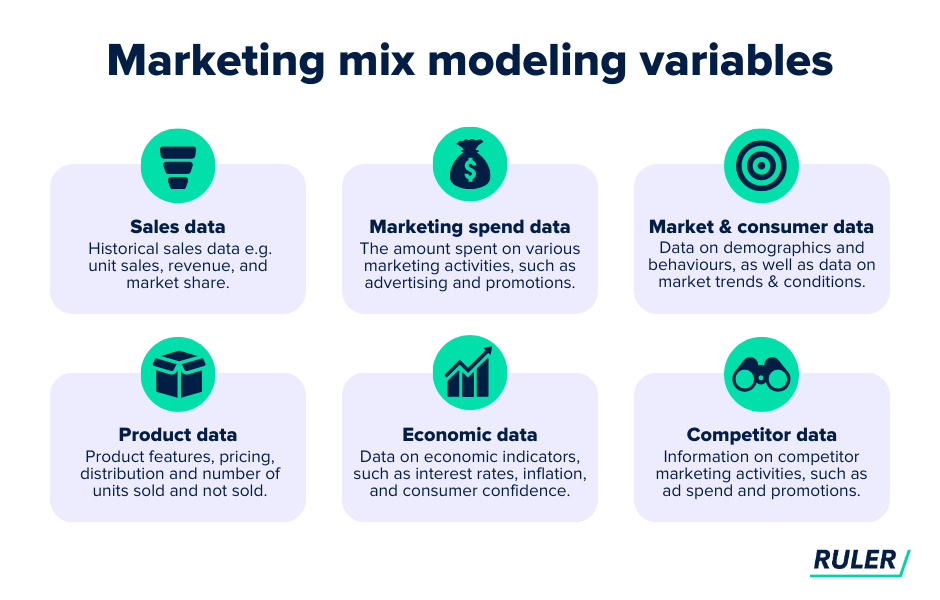
Let’s take Ruler’s marketing mix modelling, for example.
Ruler’s MMM uses the data sources listed above to show the impact of different marketing touchpoints and identifies the point at which additional investment in a marketing channel will no longer result in a proportional increase in sales or revenue.
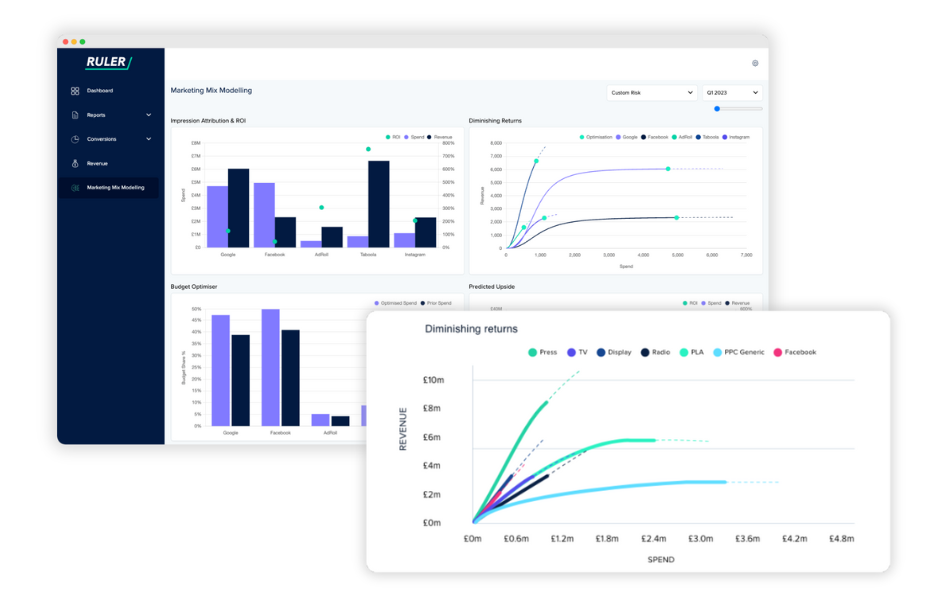
While it may seem like doubling your PPC ad spend from £0.6m to £1.2m would double your conversions, in reality, your returns will likely diminish as you increase your ad spend.
This is because there is a point at which additional investment in PPC will no longer result in a proportional increase in conversions.
Diminishing returns is just one benefit of MMM too. Other benefits include the ability to:
More on Ruler shortly, first let’s take a deeper dive into how the concept of MMM works…
💡 Skip ahead to the demo
If you’re ready to learn how Ruler can help you improve your marketing ROI, book a demo and see for yourself all the good stuff we have to offer.
Chat with us and see Ruler in action
Marketing mix modeling uses the principle of multi-linear regression (MLR). Multiple linear regression is a statistical technique used to model the linear relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
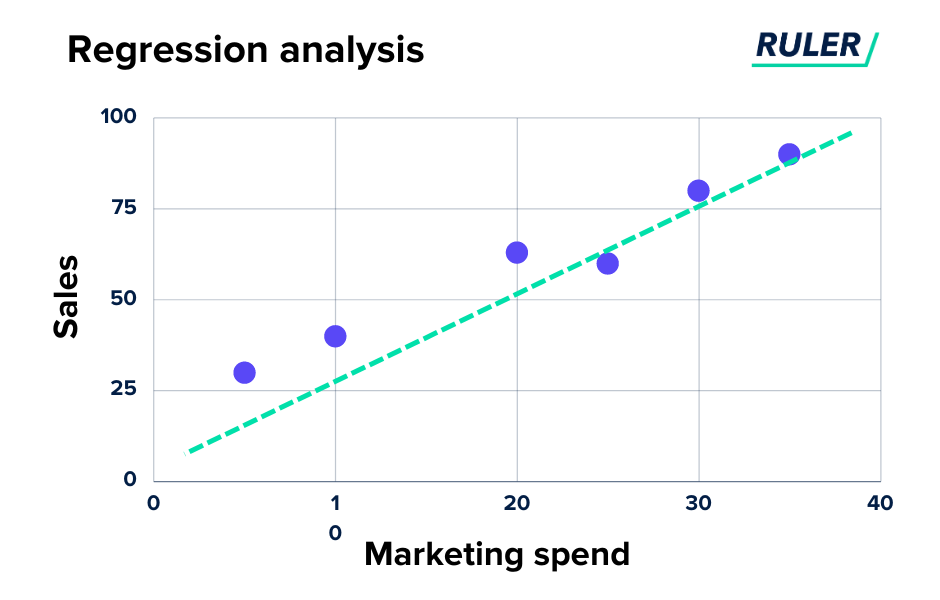
With MLR, you can estimate the impact of each independent variable on the dependent variable and make reliable predictions about the impact of future changes to the marketing mix.
If you’re new to marketing mix modeling, you’re probably wondering what the difference is between a dependent and independent variable.
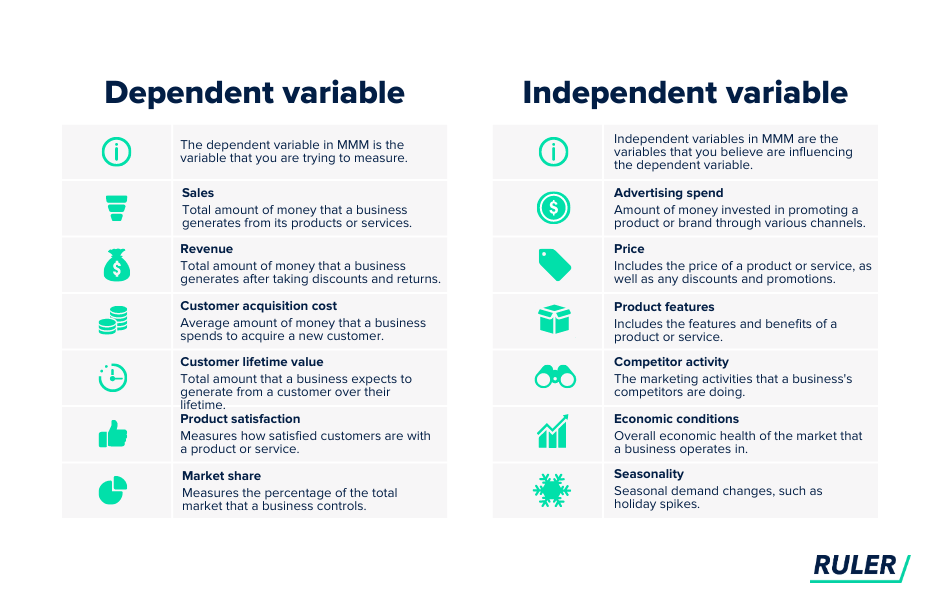
A dependent variable in MMM is typically a measure of business performance. Here are a few examples:
So what makes an independent variable? An independent variable represents the marketing mix elements that are believed to impact the dependent variable. Here are a few examples:
While MLR is a widely used method in MMM, other statistical techniques, such as time-series analysis, logistic regression, or machine learning algorithms, may also be used depending on the specific needs and goals of the analysis.
At this point, you’re probably wondering why you should even bother with marketing mix modelling?
Chances are you’re already using multi-touch attribution to generate insights and guide your own marketing strategy. But the truth is that no single marketing measurement method is enough to provide a complete picture of your marketing effectiveness.
Each marketing measurement technique has its own strengths and weaknesses, providing a different kind of “truth”.
Take multi-touch attribution, for example.
Multi-touch attribution is great for providing granular insights on individual marketing touchpoints, but it relies heavily on click path data and cookies, which are becoming increasingly redundant.
It misses the impact of invisible touchpoints (e.g. ad impressions and TV views), which can lead to an incomplete understanding of the customer journey.
Even though we’re an attribution and MMM vendor, we believe that you need a combination of different methods to triangulate the truth and gain a holistic view of marketing performance.
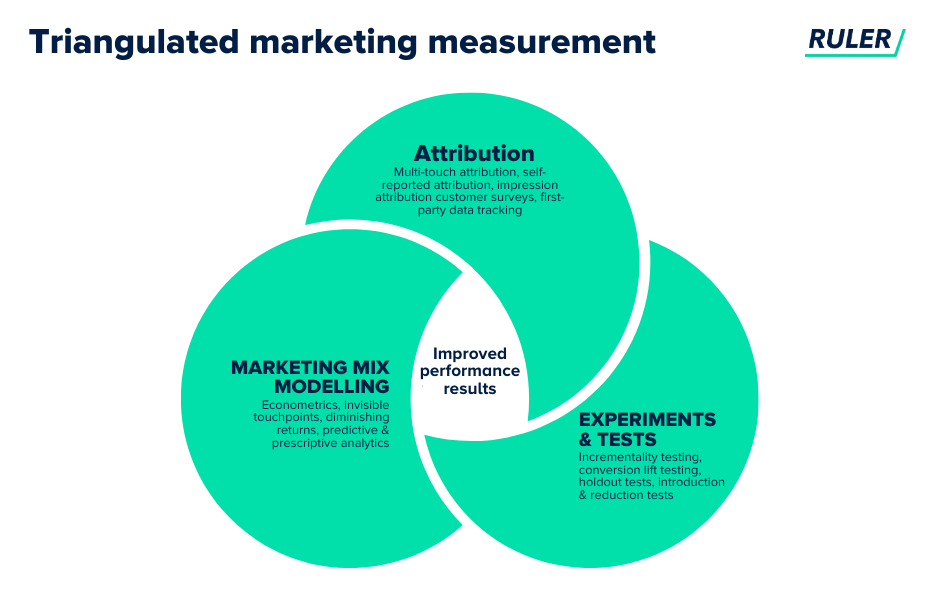
Methods like multi-touch attribution, MMM, and incrementality testing all have their flaws. But, when used together, they can complement each other’s strengths and weaknesses to provide you with the bigger picture.
Marketing mix modeling is often compared to marketing attribution, but they’re actually quite different. They’re both related but have distinct analytical approaches for evaluating the impact of marketing on business performance.
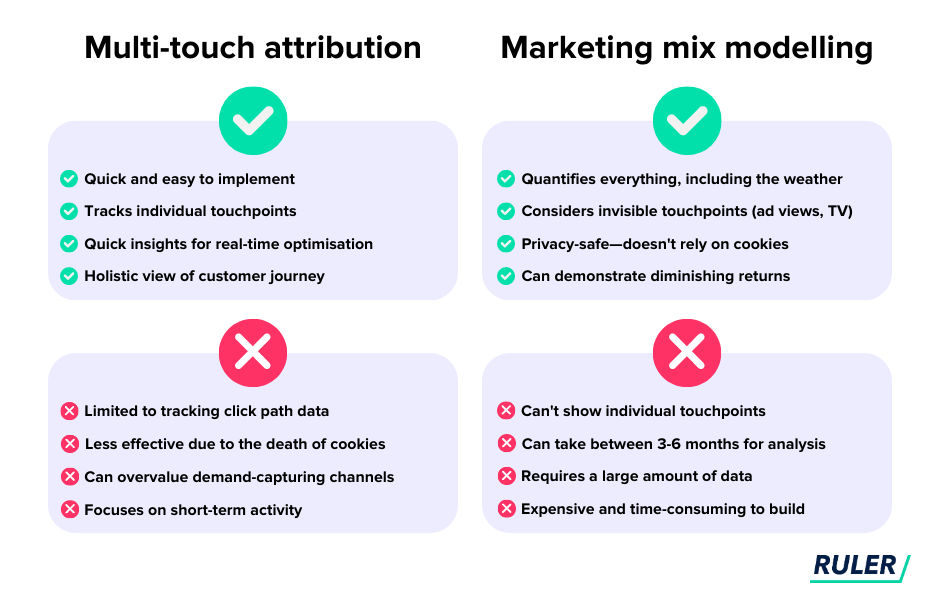
Marketing attribution is the process of assigning credit for a sale or conversion to the specific marketing touchpoints (e.g. ads, email, website) that contributed to the outcome.
Multi-touch attribution, in particular, uses various models to determine the contribution of each touchpoint and assigns credit to the interactions that had the most impact on the final conversion.
Related: What is multi-touch attribution and how does it work?
Multi-touch attribution, in particular, uses various models to determine the contribution of each touchpoint and assigns credit to the interactions that had the most impact on the final conversion or sale.
Here are a few examples of MTA models:
These are just a few examples of commonly used marketing attribution models. The choice of attribution model will depend on the specific goals and objectives of the organisation and the type of data available for analysis.
It’s also possible to use a combination of attribution models to create a custom model that combines elements of different models.
We’ve already covered marketing mix modeling and how it works. To recap it’s a statistical technique used in marketing to analyse the impact of various marketing inputs on sales and other business-related metrics.
But there’s one thing we haven’t yet pointed out.
Unlike marketing attribution, MMM uses a broader approach to marketing measurement. MMM often incorporates marketing attribution as one of the inputs in its analysis. So you can think of marketing attribution as a subset of MMM.
Marketing attribution information can be used in MMM to better understand the effectiveness of different marketing channels and how they work together to drive sales.
This information can then be incorporated into MMM’s analysis to provide a more comprehensive view of the impact of marketing activities on business outcomes.
Marketing mix modeling has become an increasingly popular and important tool for marketers, especially with the “cookie apocalypse” approaching fast. It’s estimated that 40% of Fortune 500 companies already use marketing mix modeling technology.
To get started with MMM, you need to gather and organise your data, decide which models to use, and set up the system.
These steps typically include:
These steps sound simple, but in practice, it’s quite difficult to set up successfully, especially if you’re new to the principle of marketing mix modeling.
Another option is to invest in an attribution and MMM solution. It’s less complicated and often more cost-effective than having to hire a statistician to build a marketing mix modeling system from scratch.
Take Ruler Analytics, for example.
Ruler takes the best of multi-touch attribution and marketing mix modeling to help you better understand your marketing performance and identify areas to prioritise.
It lets you see how all of your channels (online and offline) are performing and how well they can be attributed to conversions and sales.
At Ruler, we’re on a mission to blend marketing attribution and marketing mix modeling to create a hybrid approach to marketing measurement.
This allows marketers to:
But how does Ruler work? Let’s dive deeper into its technology.
Ruler starts by tracking the entire customer journey at the visitor level on a first-party basis.
It captures the marketing source from each session, page views, UTM variables, Click IDs, and Cookie IDs which are then matched to a lead driven from a form, phone call or live chat.
Ruler passes the marketing source data you’ve captured on your leads to your CRM and other marketing tools. This allows you to enrich your leads and opportunities with attribution data so you can see exactly how your marketing impacts pipeline generation.
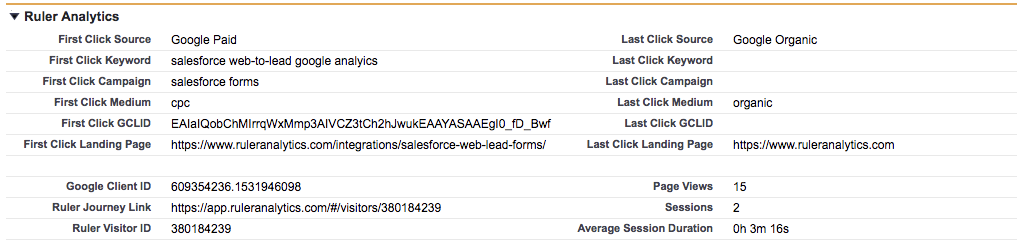
When a lead is marked as closed as won, the revenue data is sent back to Ruler. With revenue and opportunity data in Ruler, you can easily measure and validate the impact of your marketing sources, campaigns and keywords.
But there’s more yet.
Ruler isn’t just your ordinary attribution platform. It uses marketing mix modeling alongside its multi-touch attribution technology to give you the bigger picture and help you understand the factors that affect your sales and ROI.
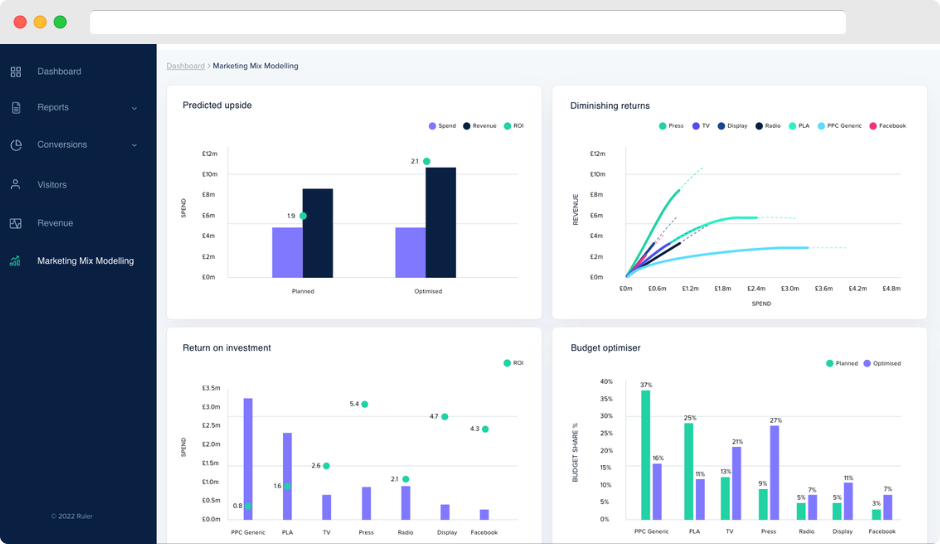
There are the five core features of Ruler’s MMM:
1. Impression attribution modeling. Ruler’s impression attribution gives you more insight into your invisible touchpoints e.g. views, tv and radio impressions. A good example would be when a user is served an ad, and then instead of clicking, they go directly to your website to convert into a lead or customer. With Ruler’s impression modeling, you can better understand when, where, and how people are seeing your ads and offline initiatives.
2. Diminishing returns. We covered this earlier, but due to the way impression impact is calculated using diminishing return curves, Ruler is able to model your ROI over time and project how much headroom is still left in your advertising channels.
3. Budget optimiser. Ruler’s budget optimiser uses diminishing returns to identify the optimal spend for each marketing channel. It does this by shifting recommended budget from channels that have reached the point of diminishing returns to those that have not, such as from Google search to print advertising.
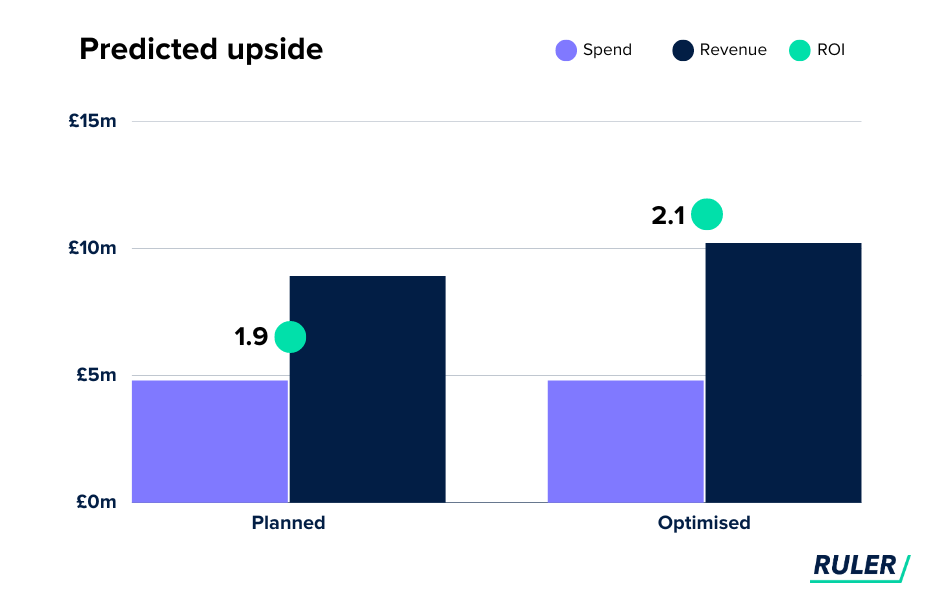
4. Predicted upside. The budget optimiser shows how your reallocated spend will impact your sales and revenue. In the example below, you could expect an additional £1.3 million in sales, which will increase your ROI from £1.9 million to £2.1 million.
Book a demo of Ruler to see it in action for yourself here.
With marketing mix modeling set up successfully, you’ll have data linking your sales to your marketing efforts.
You’ll be able to see a clear picture of your marketing wins (and losses), so you can improve and optimise your marketing strategy for maximum results.
If you’re looking for a marketing reporting system that unifies data across online and offline channels and links your conversions directly to revenue, then Ruler is for you.
It allows you to access revenue data and link it directly to your marketing activities without any of the headache of doing it yourself.